Product Description
Customized OEM Forged Casting CZPT Bevel Pinion Differential Straight Spiral Helical Hypoid Spline Shaft External Grinding Teeth Spur Worm Drive Gear
Product advantages & features
(1) Accessory products of the truck, use 20CrMmti material.
(2) Heat treatment and tempering, high gear root strength, stronger impact resistance.
(3) Multi-purpose CZPT carburizing processing, fine grinding processing technology, effectively reducing noise.
(4) Test product 1 by one, and inspect each product on delivery to ensure 100% quality stability of the product.
(5) The unified brand carton, inner bag and integral foam packaging, which is strong and beautiful.
(6) Passed ISO/TS16949:2009 quality management system certification.
(7) Passed ISO/IEC17571:2005 certification.
(8) Certified by National Laboratory Accreditation Committee.
(9) “100 Auto Parts Suppliers” in China.
(10) China Machinery Top 500.
(11) National first-class measurement enterprise.
(12) National first-class physical and chemical enterprise.
Factory Show
More Products
| Truck Model | Sinotruk, Shacman, Saic Xihu (West Lake) Dis.n, Foton Auman, CZPT Xihu (West Lake) Dis., Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng, European & Japanese Truck Series, North BENZ( BEIBEN), JAC, etc. | |
| Product catalogue | Axle | Wheel Assembly |
| Differential Assembly | ||
| Main Reducer Assembly | ||
| Inner Ring Gear& Bracket | ||
| Basin Angle Gear/ Bevel Gear | ||
| Axle Shaft/ Half Shaft & Through Shaft | ||
| Axle Housing& Axle Assembly | ||
| Steering knuckle & Front Axle | ||
| Gear | ||
| Brake Drum& Wheel Hub | ||
| Flange | ||
| Bearing | ||
| Main Reducer Housing | ||
| Oil Seal Seat | ||
| Nut& Shim Series | ||
| Brake Backing Plate | ||
| Chassis Support Products | Leaf Spring Bracket | |
| Drop Arm Series | ||
| Bracket Series | ||
| Leaf Spring Shackle Series | ||
| Balanced Suspension Series | Balance Shaft Assembly | |
| Balance Shaft Housing | ||
| Axle Spring Seat | ||
| Thrust Rod | ||
| Balance Shaft Parts | ||
| Shock Absorber Series | Shock Absorber | |
| Shock Absorbing Airbag | ||
| Steering System | Power Steering Pump | |
| Power Steering Gear | ||
| Rubber Products | Oil Seal | |
| Rubber Support | ||
| Thrust Rod Rubber Core | ||
| Truck Belt | ||
| Engine support | ||
| Other | ||
| Clutch Series | Clutch Pressure Plate | |
| Clutch Disc | ||
| Flywheel Assembly | ||
| Flywheel Ring Gear | ||
| Adjusting Arm Series | ||
Working Principle
Single reduction gear is a driving bevel gear (commonly known as angular gear) and a basin angle gear pair. The driving bevel gear is connected with the transmission shaft, rotates clockwise, sticks to its right side from the bevel gear, and rotates downward at the meshing point, which is consistent with the CZPT direction of the wheel. Due to the small diameter of the driving bevel gear and the large diameter of the bevel gear, the function of deceleration is achieved.
The double reduction has an additional intermediate transition gear.The left side of the driving bevel gear is meshed with the bevel gear of the intermediate gear. The bevel gear is coaxial with a spur gear with small diameter, and the spur gear is meshed with the driven gear. In this way, the intermediate gear rotates backward and the driven gear rotates forward. There is a two-stage deceleration process in the middle.
Due to the increase of axle volume, double reduction was mainly used in vehicles with low engine power in the past, mainly in construction machinery with low speed and high torque.
In the double reduction final drive, if the second-stage deceleration is carried out near the wheel, it actually constitutes an independent part at the 2 wheels, it is called wheel reducer. The advantage of this is that the torque transmitted by the half shaft can be reduced, which is conducive to reducing the size and quality of the half shaft. The wheel reducer can be planetary gear type or composed of a pair of cylindrical gear pairs. When the cylindrical gear pair is used for wheel side deceleration, the up-down position relationship between the wheel axis and the half shaft can be changed by adjusting the mutual position of the 2 gears. This kind of axle is called portal axle, which is often used for vehicles with special requirements for the high and low position of the axle.
According to the number of the main reducer transmission ratio, it can be divided into single-speed and double-speed.
Domestic cars basically adopt single speed main reducer with fixed transmission ratio. On the double reduction final drive, there are 2 transmission ratios for selection, and this main reducer actually acts as an auxiliary transmission.
Packaging & Shipping
Certifications
FAQ
Q1. How to guarantee your after-sales service?
Strict inspection during production, Strictly check the products before shipment to ensure our packaging in good condition. Track and receive feedback from customer regularly. Our products warranty is 365 days.
Each product provides quality assurance service. If there is a problem with the product within the warranty period, the customer can negotiate with us in detail about the related claims, and we will do our best to satisfy the customer.
Q2. How can I accurately buy the products I need?
We need accurate product number, If you can’t provide product number, you can send us your product picture, or tell us your truck model, engine name plate, and so on. we will
determine exactly what you need products.
Q3. Do you accept third party inspection?
Yes.we do
Q4. How about your delivery time?
Generally, it will take 3 to 10 days after receiving your advance payment. The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
Q5. What are your brand agency conditions and advantages?
After we CZPT an agent in 1 city, we will not CZPT a second company to protect the agent’s brand advantage and price advantage. And we will help the agent develop customers and solve all kinds of difficult and miscellaneous problems about products.
Q6. What is your terms of payment?
By TT or LC. We’ll show you the photos of the products and packages before you pay the balance.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| Application: | Heavy Duty Truck Parts |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | Internal Gear, External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 25/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
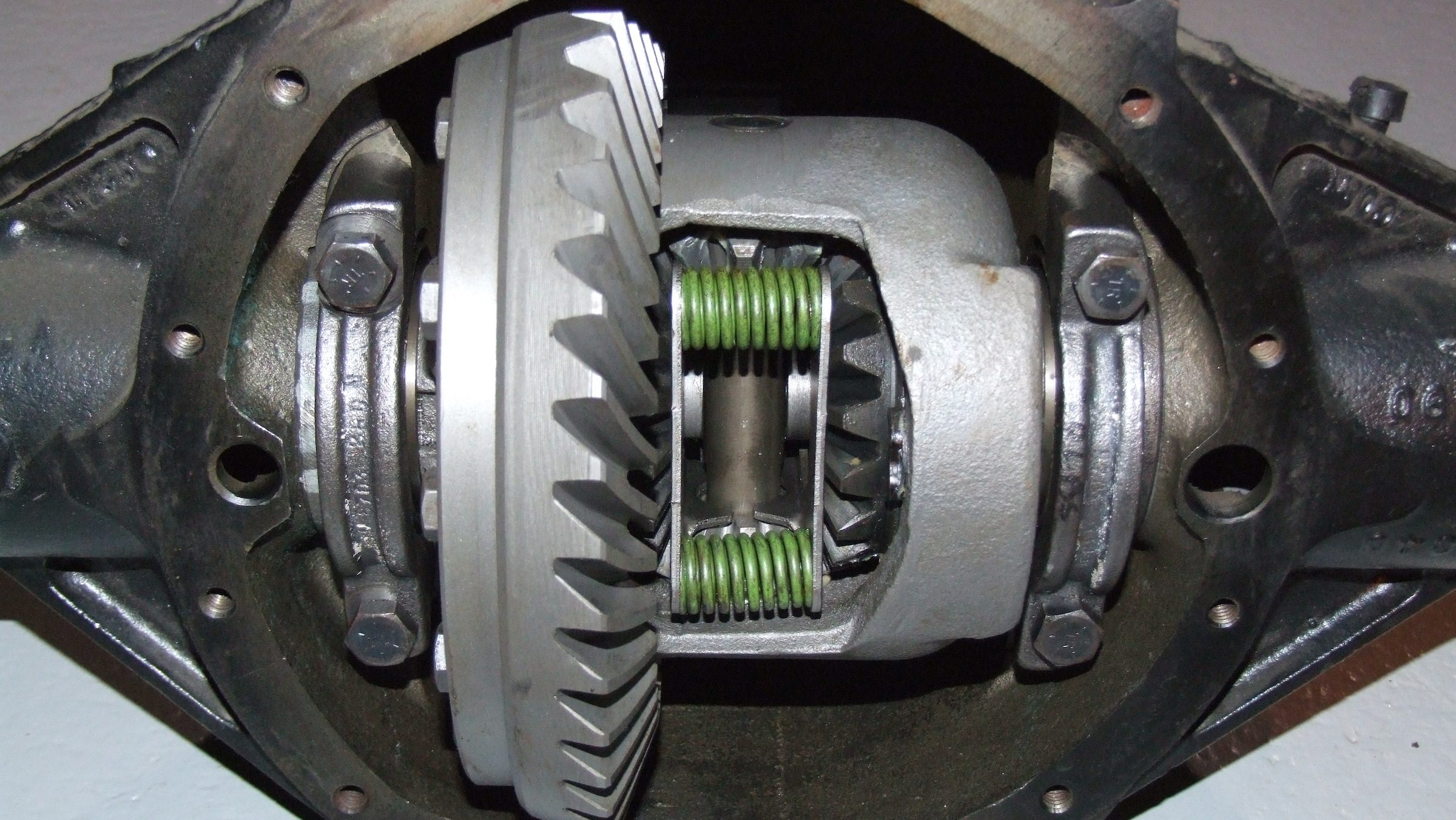
What are the symptoms of a failing differential gear?
A failing or faulty differential gear can exhibit various symptoms that indicate potential problems with its operation. Here are some common signs to look out for:
- 1. Whining or Howling Noises: A prominent symptom of a failing differential gear is the presence of whining, howling, or rumbling noises coming from the rear of the vehicle. These noises may increase with vehicle speed or during specific driving maneuvers, such as turning or accelerating. The noises can indicate worn or damaged gears, insufficient lubrication, or misalignment within the differential assembly.
- 2. Clunking or Clicking Sounds: Another symptom of a failing differential gear is the occurrence of clunking or clicking sounds, particularly during changes in direction or when shifting between drive modes. This can indicate worn or damaged gears, worn universal joints, or loose components within the differential.
- 3. Vibration or Shuddering: A failing differential gear may cause vibration or shuddering sensations, especially when accelerating or decelerating. This can be a result of worn or damaged gears, improper gear meshing, or worn bearings within the differential assembly.
- 4. Difficulty in Turning: If the differential gear is experiencing issues, you may notice increased difficulty in turning the vehicle, particularly during sharp turns or low-speed maneuvers. This can be caused by uneven torque distribution or limited mobility of the differential gears.
- 5. Fluid Leaks: Leaking fluid around the differential housing is a potential indicator of a failing gear. Differential fluid is essential for lubrication and cooling of the gears and bearings. A leak can result from worn seals, cracked housing, or damaged components within the differential assembly.
- 6. Excessive Tire Wear: A failing differential gear may lead to uneven tire wear. If you notice significant wear on the inner or outer edges of the tires, it could be a sign of differential problems. Uneven torque distribution can cause increased stress on specific tires, leading to abnormal wear patterns.
- 7. Gear Slippage: In severe cases, a failing differential gear may result in gear slippage. This means that power is not being effectively transferred to the wheels, causing a loss of traction and reduced vehicle performance. Gear slippage can occur due to worn or damaged gears, insufficient lubrication, or other internal failures within the differential.
If you observe any of these symptoms, it is recommended to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic or technician. They can diagnose the exact cause of the issues and determine if the differential gear requires repair or replacement.
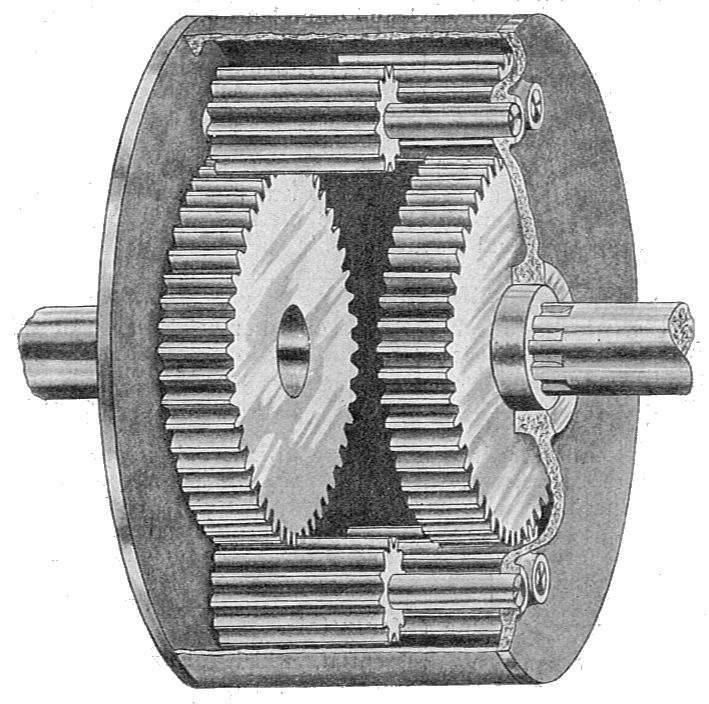
How do differential gears function in both front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles?
In both front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles, differential gears serve the same fundamental purpose of distributing power from the engine to the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds. However, their specific configurations and functions differ between these two types of drivetrains. Here’s a detailed explanation of how differential gears function in both front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles:
Front-Wheel-Drive Vehicles:
In front-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are typically integrated into the transaxle assembly, which combines the transmission and differential into a single unit. Here’s how the differential gears function in front-wheel-drive vehicles:
- Power Input: The engine’s power is transmitted through the transmission to the transaxle assembly.
- Ring and Pinion Gears: The power from the transaxle is delivered to a set of ring and pinion gears within the differential assembly. These gears are responsible for distributing torque to the front wheels.
- Spider Gears: The ring gear is connected to a carrier that houses multiple smaller gears called spider gears. These spider gears allow the front wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns.
- Equal Torque Distribution: In front-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears prioritize equal torque distribution between the two front wheels. This design helps maintain traction and stability during acceleration and cornering.
- Traction Control: Some front-wheel-drive vehicles may also incorporate additional features in the differential assembly, such as electronic limited-slip differentials or traction control systems. These features help optimize traction by transferring power to the wheel with better grip, reducing wheel spin and improving overall performance.
Rear-Wheel-Drive Vehicles:
In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are typically located in the rear axle assembly. Here’s how the differential gears function in rear-wheel-drive vehicles:
- Power Input: The engine’s power is transmitted through the transmission to the driveshaft, which connects to the rear axle assembly.
- Drive Pinion and Ring Gear: The driveshaft is connected to a drive pinion gear, which meshes with a larger ring gear. This gear set is responsible for transferring power to the rear wheels.
- Spider Gears: Similar to front-wheel-drive vehicles, rear-wheel-drive vehicles also have spider gears housed within the differential assembly. The spider gears allow the rear wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns.
- Torque Distribution: In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears distribute torque to the rear wheels in a manner that prioritizes rear-wheel traction and propulsion. This configuration is particularly beneficial for vehicle acceleration and load-carrying capability.
- Enhanced Features: Rear-wheel-drive vehicles may also incorporate advanced differential systems, such as limited-slip differentials or electronic locking differentials, to optimize traction and performance. These features help improve grip, especially in challenging driving conditions or when driving off-road.
In summary, differential gears function differently in front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles due to their distinct drivetrain configurations. In front-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are typically integrated into the transaxle assembly and prioritize equal torque distribution to the front wheels. In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are located in the rear axle assembly and focus on torque distribution to the rear wheels for propulsion. Understanding the specific functions of differential gears in each drivetrain type is essential for optimizing vehicle performance, traction, and stability.
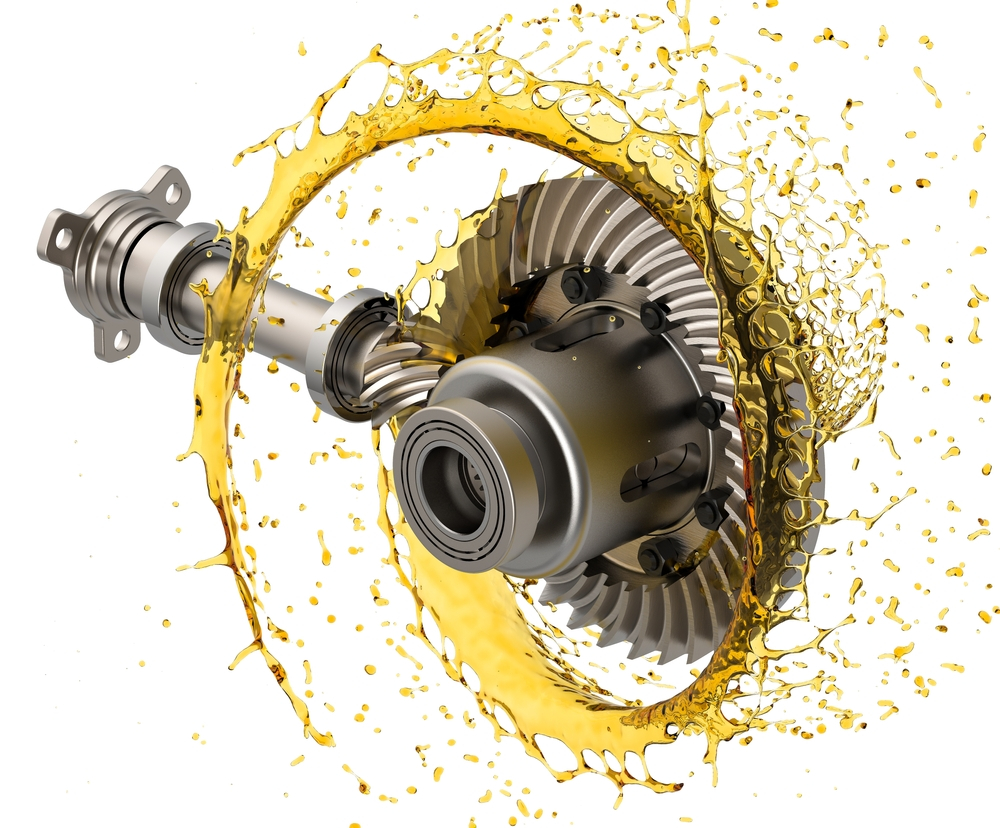

Can you explain the concept of torque distribution in a differential gear?
Torque distribution is a fundamental concept in a differential gear that refers to the way rotational force is distributed among the wheels of a vehicle. Here’s a detailed explanation:
In a vehicle equipped with a differential gear, torque is transmitted from the engine to the differential, and then further distributed to the wheels. The differential gear ensures that torque is divided between the wheels, allowing them to receive power and propel the vehicle forward.
1. Power Input:
The torque distribution process begins with the power input from the engine. The engine generates rotational force, or torque, which is transmitted through the drivetrain to the differential gear.
2. Differential Assembly:
Within the differential gear, torque is distributed among several components, including the ring gear, pinion gear, side gears, and spider gears. The specific arrangement may differ depending on the type of differential used.
3. Side Gears and Spider Gears:
The side gears are connected to the axle shafts, which extend to the wheels. The spider gears, also known as planetary gears, are positioned between the side gears. When torque is applied to the differential assembly, it is transferred to the side gears through the spider gears.
4. Equal Torque Distribution:
In a straight-line driving scenario, where both wheels have equal traction and are rotating at the same speed, the spider gears rotate freely on their respective shafts. This allows the side gears to rotate at the same speed as the differential case, resulting in equal torque distribution to both wheels. As a result, both wheels receive an equal share of power from the differential.
5. Unequal Torque Distribution:
During turns or when one wheel encounters different traction conditions, the wheels need to rotate at different speeds. In this situation, the spider gears are forced to rotate along with the side gears due to the difference in rotational speeds between the two wheels.
As the spider gears rotate, they allow the side gears to rotate at different speeds, compensating for the variation in wheel speeds. This results in unequal torque distribution, with the outer wheel (on the outside of the turn) receiving more torque and the inner wheel (on the inside of the turn) receiving less torque. The differential gear enables this torque differentiation, ensuring that the wheels can rotate independently while still receiving power from the differential.
6. Optimizing Traction:
The torque distribution in a differential gear plays a crucial role in optimizing traction. Unequal torque distribution allows the wheel with better traction to receive more power, maximizing the vehicle’s ability to maintain forward motion. This is particularly beneficial in situations where one wheel is on a slippery surface or encounters reduced traction conditions.
7. Differential Types:
It’s important to note that different types of differentials can provide varying torque distribution characteristics. For example, open differentials primarily distribute torque equally, while limited-slip differentials and locking differentials offer varying degrees of torque biasing to improve traction in specific conditions.
In summary, torque distribution in a differential gear refers to the division of rotational force among the wheels of a vehicle. The differential gear enables equal torque distribution during straight-line driving and unequal torque distribution during turns or varied traction conditions. By optimizing torque distribution, the differential gear ensures efficient power delivery, traction optimization, and overall performance of the vehicle.


editor by CX 2023-09-04