Product Description
Our advantage:
*Specialization in CNC formulations of high precision and quality
*Independent quality control department
*Control plan and process flow sheet for each batch
*Quality control in all whole production
*Meeting demands even for very small quantities or single units
*Short delivery times
*Online orders and production progress monitoring
*Excellent price-quality ratio
*Absolute confidentiality
*Various materials (stainless steel, iron, brass, aluminum, titanium, special steels, industrial plastics)
*Manufacturing of complex components of 1 – 1000mm.
Production machine:
| Specification | Material | Hardness |
| Z13 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z16 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z18 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z20 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z26 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z28 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Custom dimensions according to drawings | Steel | HRC35-40 |
Production machine:
Inspection equipment :
Gear tester
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | Internal Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Rolling Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Steel |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
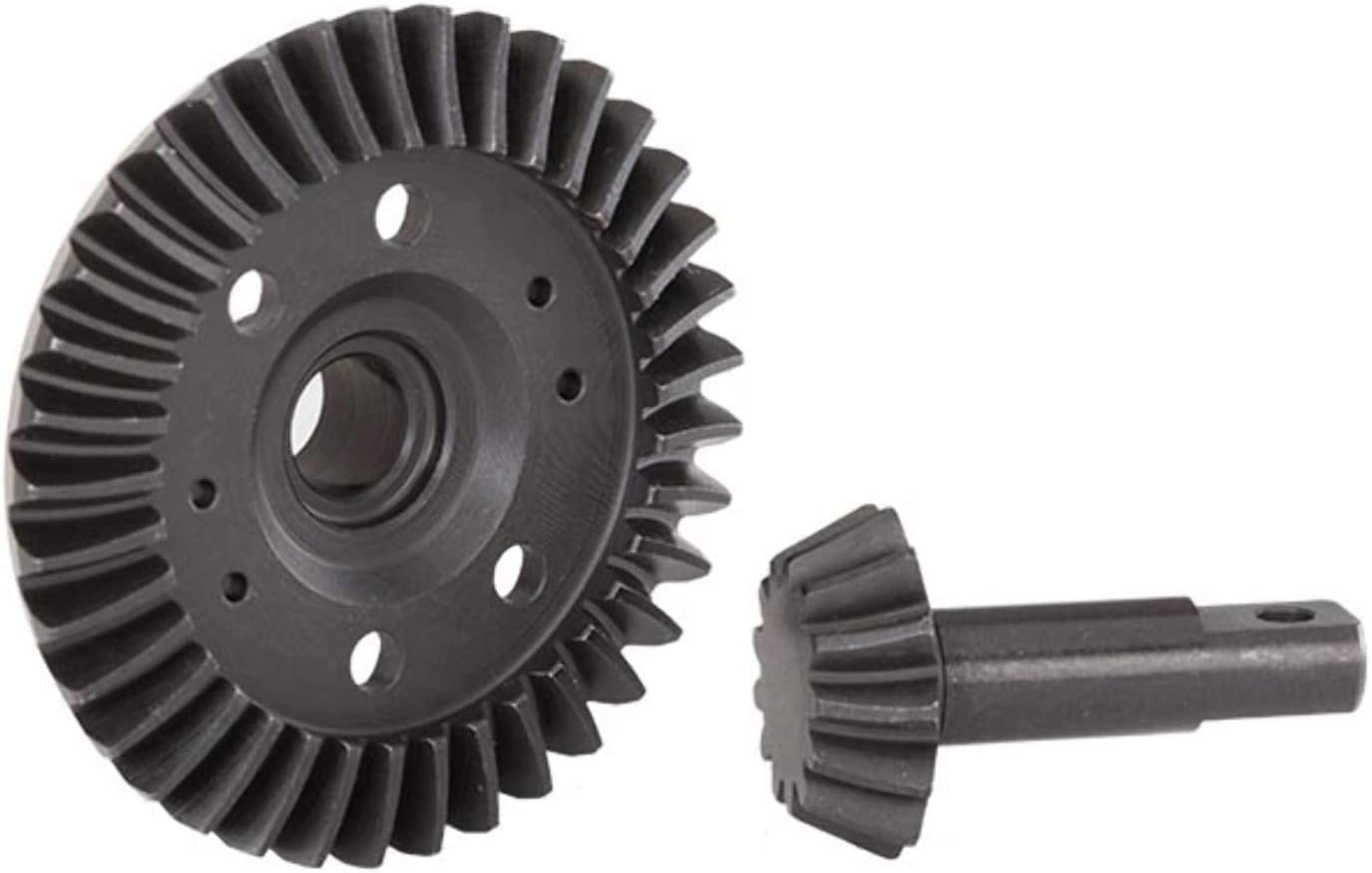

How does a differential gear system contribute to tire longevity?
A differential gear system plays a crucial role in tire longevity by ensuring optimal traction, minimizing tire wear, and distributing torque effectively. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a differential gear system contributes to tire longevity:
- 1. Traction Optimization: The differential gear system allows the wheels on the same axle to rotate at different speeds when the vehicle is turning. This capability helps improve traction and reduces tire scrubbing, which occurs when the tires resist turning and skid instead. By optimizing traction during turns, the differential gear system helps prevent excessive tire wear caused by scrubbing.
- 2. Torque Distribution: The differential gear system distributes torque from the engine to the wheels, allowing each wheel to receive an appropriate amount of power based on traction conditions. This distribution helps prevent wheel spin and excessive tire wear. By ensuring that torque is evenly distributed, the differential gear system helps maintain balanced tire wear across all wheels.
- 3. Wheel Speed Synchronization: When driving in a straight line, the differential gear system synchronizes the rotational speeds of the wheels. This synchronization minimizes tire scrubbing and reduces uneven wear. By keeping the wheels rotating at similar speeds, the differential gear system promotes even tire wear, extending tire longevity.
- 4. Cornering Stability: During cornering, the differential gear system allows the outer wheel to rotate faster than the inner wheel. This speed difference is necessary to accommodate the varying distances each wheel travels around the curve. By enabling smooth and controlled cornering, the differential gear system helps prevent excessive tire wear caused by lateral forces.
- 5. Reduced Stress on Tires: A properly functioning differential gear system helps reduce stress on tires by allowing them to rotate freely and independently. By mitigating excessive forces and minimizing tire scrubbing, the differential gear system helps decrease wear and tear on the tires. This reduction in stress contributes to prolonged tire life.
- 6. Traction Control: Some modern vehicles are equipped with advanced differential systems, such as electronic limited-slip differentials or torque vectoring differentials. These systems actively manage torque distribution to individual wheels based on traction conditions. By optimizing traction control, these differential systems help minimize tire slippage, improve grip, and reduce tire wear.
- 7. Proper Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the differential gear system is essential for tire longevity. This includes periodic inspection of the differential components, ensuring proper lubrication, and addressing any issues promptly. Well-maintained differentials help ensure optimal performance, reducing the risk of tire wear and extending tire life.
Overall, a well-functioning and properly maintained differential gear system plays a vital role in tire longevity. It optimizes traction, distributes torque effectively, synchronizes wheel speeds, promotes cornering stability, and reduces stress on tires. By understanding and maintaining the differential gear system, drivers can help maximize tire life and minimize the need for premature tire replacements.
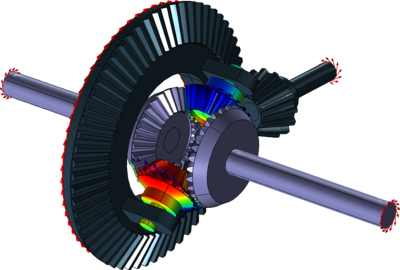
What is the role of a center differential in all-wheel-drive systems?
In an all-wheel-drive (AWD) system, the center differential plays a crucial role in distributing power between the front and rear wheels. It is responsible for managing torque transfer and ensuring optimal traction and stability in various driving conditions. Here’s a detailed explanation of the role of a center differential in all-wheel-drive systems:
- Torque Distribution: The center differential’s primary function is to distribute torque between the front and rear axles in an AWD system. It receives power from the engine and transmits it to both the front and rear wheels. The distribution of torque can vary depending on the design and capabilities of the center differential.
- Power Split: The center differential splits the engine’s power between the front and rear axles in a manner that optimizes traction and stability. Under normal driving conditions, it typically distributes torque evenly, providing balanced power to all wheels. This balanced power distribution helps enhance vehicle control and stability.
- Variable Torque Split: In some AWD systems, the center differential can vary the torque split based on driving conditions. It can adjust the distribution of power between the front and rear axles to optimize traction and handling. For example, if the system detects slippage in the front wheels, it can transfer more torque to the rear wheels to improve traction and maintain vehicle stability.
- Traction Enhancement: The center differential helps improve traction by allowing the front and rear wheels to rotate at different speeds. This capability is particularly beneficial in situations where the left and right wheels on the same axle encounter varying levels of grip, such as when driving on slippery or uneven surfaces. By allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds, the center differential enables the wheels with better traction to receive more power, enhancing overall grip and traction.
- Adaptability to Different Conditions: A well-designed center differential enables an AWD system to adapt to different driving conditions. Whether it’s driving on dry pavement, wet roads, icy surfaces, or off-road terrain, the center differential helps optimize power distribution to maintain traction and stability. It allows the AWD system to provide enhanced grip and control, regardless of the prevailing driving conditions.
- Integration with Other Systems: The center differential often works in conjunction with other vehicle systems to further enhance performance and safety. For example, some AWD systems incorporate electronic controls that can interact with the vehicle’s stability control system, traction control system, or other safety features. This integration helps optimize power delivery, traction management, and overall vehicle dynamics.
In summary, the center differential plays a critical role in all-wheel-drive systems. It distributes torque between the front and rear axles, enhances traction and stability, adapts to different driving conditions, and integrates with other vehicle systems. By effectively managing torque transfer, the center differential helps maximize grip, improve handling, and enhance overall performance in AWD vehicles.
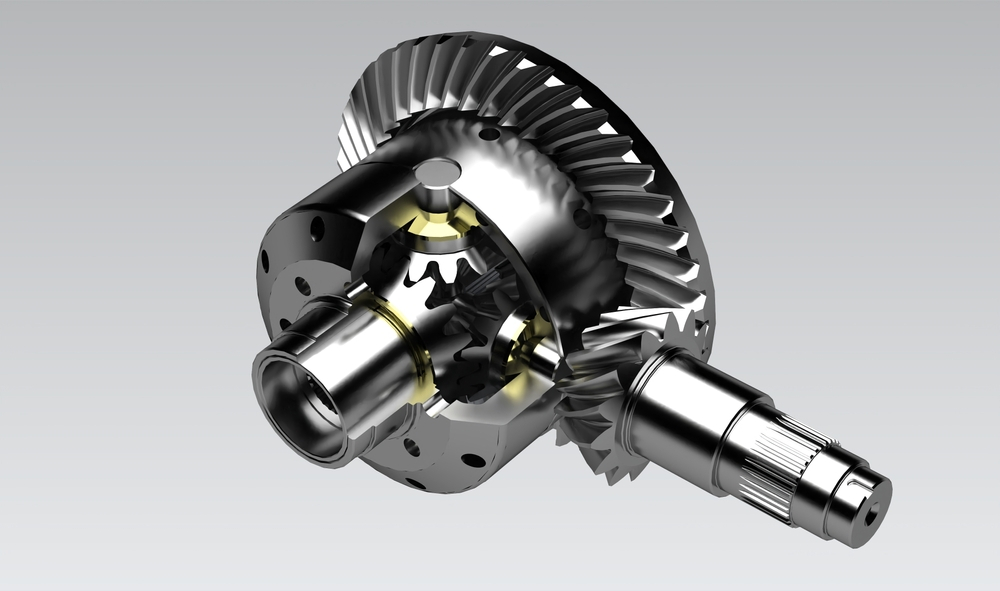
What is the purpose of using a differential gear in an automobile?
A differential gear serves a crucial purpose in an automobile. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The purpose of using a differential gear in an automobile is to allow the wheels to rotate at different speeds while receiving power from the engine. It enables smooth and controlled maneuvering, optimizes traction, and enhances overall performance. The differential gear plays several key roles in an automobile:
1. Torque Distribution:
One of the primary purposes of a differential gear is to distribute torque (rotational force) from the engine to the wheels. As the engine generates power, the differential ensures that it is transmitted to the wheels efficiently and effectively. By dividing the torque between the two wheels, the differential enables both wheels to receive power and propel the automobile forward.
2. Differential Action:
The differential gear allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds when the automobile is turning or when one wheel encounters different traction conditions. This differential action is crucial for smooth and controlled maneuvering. By enabling the outer wheel to rotate faster than the inner wheel during a turn, the differential allows the automobile to negotiate corners without binding or skidding.
3. Wheel Speed Compensation:
When the automobile is turning, the inside wheel travels a shorter distance compared to the outside wheel. Without a differential gear, this speed difference would cause significant drivetrain stress and tire wear. The differential gear compensates for the varying wheel speeds by allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing strain on the drivetrain components.
4. Traction Improvement:
In situations where one wheel loses traction, such as when driving on slippery surfaces or uneven terrain, the differential gear helps improve traction. By allowing the wheel with traction to receive more power, the differential ensures that the automobile can continue moving forward. This is particularly important in automobiles with two-wheel drive, as the differential helps optimize power delivery to the wheel with better traction.
5. Reducing Tire Wear:
The differential gear contributes to reducing tire wear by accommodating differences in wheel speeds. By allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns, the differential minimizes tire scrubbing and uneven wear. It helps distribute the forces evenly across the tires, promoting longer tire life and maintaining better overall traction.
6. Enhanced Stability and Handling:
The differential gear plays a crucial role in enhancing automobile stability and handling. By allowing the wheels to rotate independently, the differential facilitates better control during turns and maneuvering. It helps maintain proper weight distribution, prevents excessive understeer or oversteer, and promotes balanced handling characteristics.
Overall, the purpose of using a differential gear in an automobile is to enable torque distribution, facilitate smooth and controlled maneuvering, optimize traction, reduce tire wear, and enhance stability and handling. The differential gear ensures that power is efficiently delivered to the wheels while accommodating varying speed and traction conditions, resulting in improved performance and driving dynamics.


editor by Dream 2024-05-07