Product Description
| 1.Item Name: |
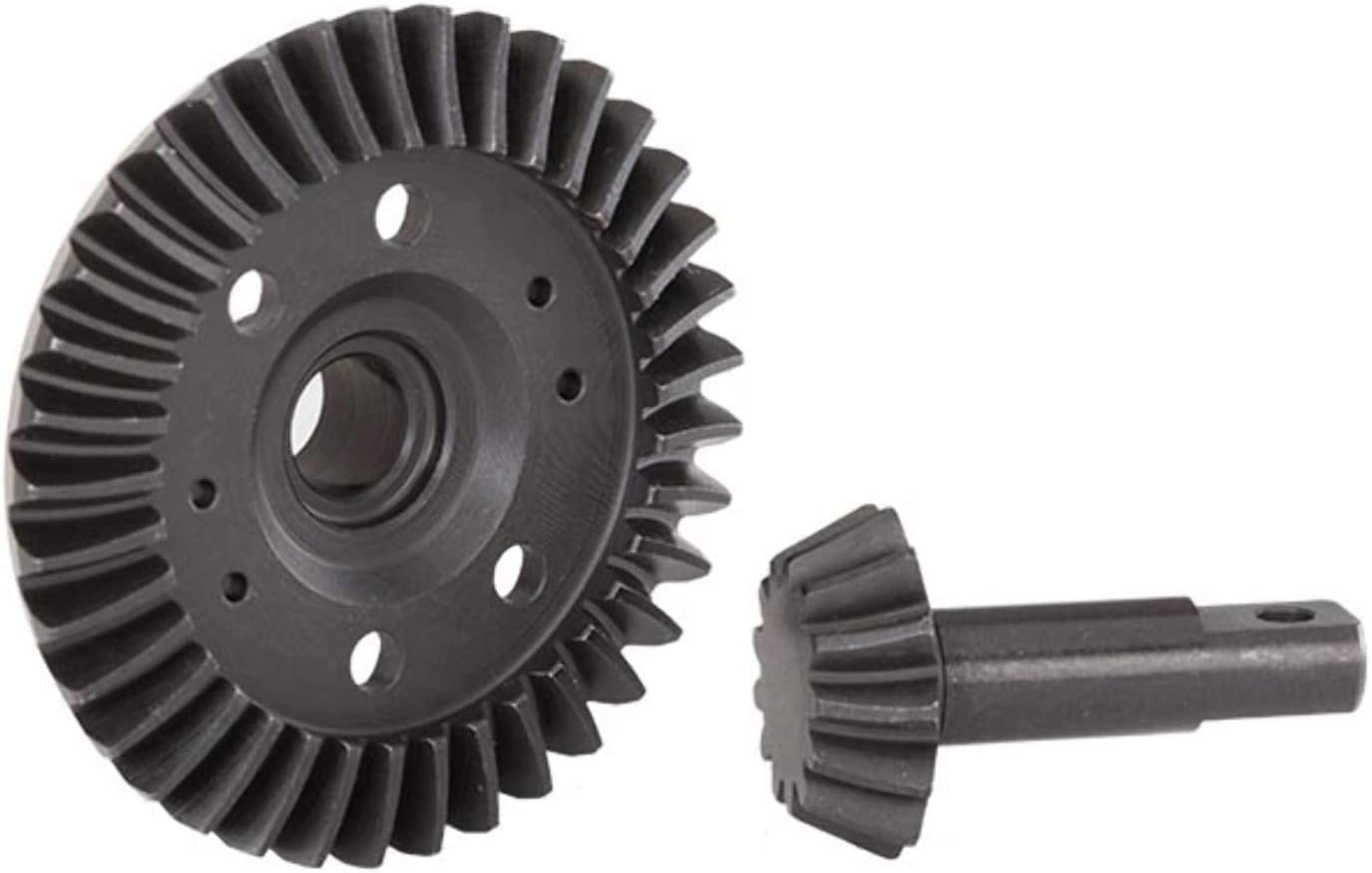
Differential side gear |
| 2.OE NO.: | M053-27-251 3647110 XM344236AA M571-27-255D 4575840 XM344215AB |
| 3.Car Make: | for Mazda B2500 |
| 4.Part Type: | chasiss system |
| 5.MOQ: | 200PCS |
| 6. Price : | EXW Price |
| 7.Shipping Way: | By Sea, DHL, UPS, FEDEX or as customers’ requirements |
| 8.Payment Terms: | Via T/T ,L/C ,Paypal ,Westerm Union,Moneygram. |
| 9.Delivery Time: | Within 30 days after deposit or as customers’ requirement |
| 10.Packaging:Packaging: |
1.Carton Box, 4.We can perform according to customer’s requirements |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 24 Hours |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Type: | Other Transmission Parts |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
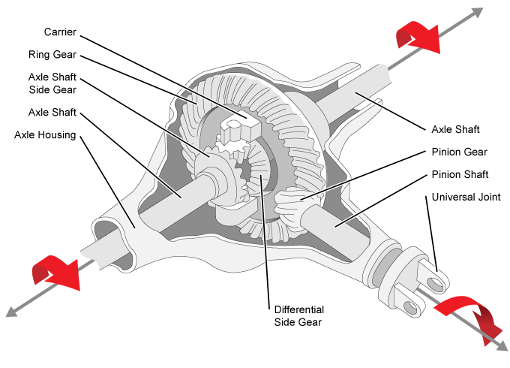
How do you address noise and vibration issues in a differential gear system?
Noise and vibration issues in a differential gear system can be concerning and may indicate underlying problems. Here are several steps that can be taken to address these issues:
- 1. Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the differential gear system for any visible signs of damage, leaks, or loose components. Check the differential housing, seals, and related components for any abnormalities. This can help identify any obvious issues that may be causing the noise or vibration.
- 2. Fluid Check: Ensure that the differential gear system has the proper amount of fluid and that the fluid is in good condition. Low or contaminated fluid can contribute to noise and vibration problems. If necessary, drain and replace the differential fluid following the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- 3. Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential for smooth operation of the differential gears. If the noise or vibration issues persist, consider applying a high-quality gear lubricant recommended by the vehicle manufacturer. Ensure that the lubricant meets the required specifications.
- 4. Tightening and Adjustment: Check for any loose fasteners or components in the differential gear system. Tighten any bolts or nuts that may have come loose. Additionally, verify that the differential gears are properly adjusted and aligned. Incorrect gear meshing or misalignment can cause noise and vibration problems.
- 5. Bearing Inspection and Replacement: Worn or damaged bearings can contribute to noise and vibration. Inspect the differential bearings for signs of wear, pitting, or excessive play. If any issues are detected, replace the faulty bearings with new ones of the appropriate size and specification.
- 6. Gear Replacement: If the differential gears themselves are worn, chipped, or damaged, they may need to be replaced. Gears with significant wear or damage can cause noise and vibration. Consult a professional mechanic or technician for an accurate assessment and to determine if gear replacement is necessary.
- 7. Seals Replacement: Damaged or worn seals can allow contaminants to enter the differential gear system, leading to noise and vibration. Replace any faulty seals to ensure a proper seal and prevent fluid leaks.
- 8. Professional Diagnosis: If the noise and vibration issues persist despite these measures, it is advisable to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or technician. They have the expertise and specialized tools to diagnose complex differential gear problems accurately. They may perform additional tests, such as a gear backlash measurement or a comprehensive inspection of the gears and bearings, to identify the source of the issues.
It’s important to address noise and vibration issues in a differential gear system promptly to prevent further damage and ensure safe and smooth vehicle operation. Regular maintenance, including fluid checks and gear inspections, can help detect potential problems early and prevent more significant issues from arising.
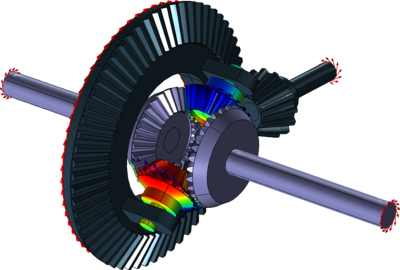
What is the role of a center differential in all-wheel-drive systems?
In an all-wheel-drive (AWD) system, the center differential plays a crucial role in distributing power between the front and rear wheels. It is responsible for managing torque transfer and ensuring optimal traction and stability in various driving conditions. Here’s a detailed explanation of the role of a center differential in all-wheel-drive systems:
- Torque Distribution: The center differential’s primary function is to distribute torque between the front and rear axles in an AWD system. It receives power from the engine and transmits it to both the front and rear wheels. The distribution of torque can vary depending on the design and capabilities of the center differential.
- Power Split: The center differential splits the engine’s power between the front and rear axles in a manner that optimizes traction and stability. Under normal driving conditions, it typically distributes torque evenly, providing balanced power to all wheels. This balanced power distribution helps enhance vehicle control and stability.
- Variable Torque Split: In some AWD systems, the center differential can vary the torque split based on driving conditions. It can adjust the distribution of power between the front and rear axles to optimize traction and handling. For example, if the system detects slippage in the front wheels, it can transfer more torque to the rear wheels to improve traction and maintain vehicle stability.
- Traction Enhancement: The center differential helps improve traction by allowing the front and rear wheels to rotate at different speeds. This capability is particularly beneficial in situations where the left and right wheels on the same axle encounter varying levels of grip, such as when driving on slippery or uneven surfaces. By allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds, the center differential enables the wheels with better traction to receive more power, enhancing overall grip and traction.
- Adaptability to Different Conditions: A well-designed center differential enables an AWD system to adapt to different driving conditions. Whether it’s driving on dry pavement, wet roads, icy surfaces, or off-road terrain, the center differential helps optimize power distribution to maintain traction and stability. It allows the AWD system to provide enhanced grip and control, regardless of the prevailing driving conditions.
- Integration with Other Systems: The center differential often works in conjunction with other vehicle systems to further enhance performance and safety. For example, some AWD systems incorporate electronic controls that can interact with the vehicle’s stability control system, traction control system, or other safety features. This integration helps optimize power delivery, traction management, and overall vehicle dynamics.
In summary, the center differential plays a critical role in all-wheel-drive systems. It distributes torque between the front and rear axles, enhances traction and stability, adapts to different driving conditions, and integrates with other vehicle systems. By effectively managing torque transfer, the center differential helps maximize grip, improve handling, and enhance overall performance in AWD vehicles.

What is a locking differential, and when is it used?
A locking differential is a specialized type of differential gear that provides maximum traction in challenging driving conditions. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Definition:
A locking differential, also known as a locker, is a mechanism that locks the rotation of the two wheels on an axle together, ensuring they both receive equal torque simultaneously. Unlike open differentials or limited-slip differentials, which allow the wheels to rotate at different speeds, a locking differential forces both wheels to turn together, regardless of traction conditions.
Function:
The primary function of a locking differential is to maximize traction. By mechanically linking the two wheels on an axle, a locking differential ensures that both wheels receive an equal amount of torque, regardless of the traction available to each wheel. This feature is particularly useful in off-road or extreme driving conditions where maintaining traction on all wheels is crucial.
Usage:
A locking differential is typically used in situations where improved traction is essential. Here are some scenarios where a locking differential is commonly employed:
1. Off-Road Driving:
Off-road enthusiasts often encounter challenging terrains with uneven surfaces, deep mud, rocks, or slippery conditions. In these situations, a locking differential can provide maximum traction by ensuring that both wheels on an axle rotate together. This helps prevent wheel spin and increases the likelihood of successfully navigating through difficult obstacles.
2. Rock Crawling:
Rock crawling involves traversing over large rocks and boulders, where maintaining traction is crucial. A locking differential allows both wheels to maintain contact with the ground simultaneously, providing better grip and stability. This enables the vehicle to crawl over rocks with minimal wheel spin and improved control.
3. Towing and Hauling:
When towing or hauling heavy loads, a locking differential can enhance traction and stability. The additional torque applied to both wheels helps prevent wheel slip and provides better power transfer to the ground. This is particularly useful in situations where the load may affect weight distribution and traction on the drive wheels.
4. Extreme Weather Conditions:
In certain weather conditions such as deep snow, ice, or mud, a locking differential can offer improved traction. By ensuring that both wheels on an axle rotate together, a locking differential helps mitigate wheel slip and enhances the vehicle’s ability to maintain forward momentum even in low-traction environments.
5. Off-Road Racing:
In off-road racing, where high-performance vehicles face demanding terrains and aggressive maneuvers, locking differentials are often utilized. The maximum traction provided by a locking differential allows for better acceleration, cornering, and overall performance in challenging racing conditions.
It’s important to note that while a locking differential offers superior traction, it can also negatively impact handling and maneuverability on paved surfaces. Due to the locked wheel rotation, turning becomes more difficult, and tire scrubbing may occur. Therefore, locking differentials are predominantly used in specialized applications or off-road vehicles designed for demanding environments.
In summary, a locking differential is a mechanism that locks the rotation of both wheels on an axle together, maximizing traction in challenging driving conditions. It is commonly used in off-road driving, rock crawling, towing and hauling, extreme weather conditions, and off-road racing, where maintaining traction is crucial for performance and stability.


editor by CX 2024-04-17