Product Description
Products description
|
Product Type |
M0.5~M12, Z8~80. standard gear, or according customer drawing to make. |
|
Material: |
Carbon Steel, Brass, Aluminium, Stainless steel, Plastic, POM, Delrin, Titanium Alloy etc. |
|
Process method |
CNC Turning, milling ,drilling, grinding etc. |
|
Surface finish: |
Chrome plating, Anodization, Powder coating, blackening, Sand blasting, Brushing & ploshing,Electrophoresis etc. |
|
OEM & ODM Service |
Available |
|
Design Software |
PRO/E, Auto CAD, Solid Works |
|
Trade Terms: |
FOB,,CIF,EXW |
|
Payment Terms: |
T/T, L/C, |
|
Packing: |
Foam, Carton, Standard Wooden boxes |
|
Capacity |
8,000~1,5000 pcs per month |
|
Delivery |
20-30 days after receiving PO |
|
Applications |
Automotive Parts,hydraulics, compressors,Industrial equipments, transmission parts, etc. |
|
Our services: |
CNC Machining, Milling, Stamping, Sheet metal fabricating, and Die-Casting |
Our Company
Gear inspection
FAQ
Q: Are you trading company or manufacturer ?
A: We are factory.
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: Generally it is 5-10 days if the goods are in stock. or it is 15-20 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to quantity.
Q: Do you provide samples ? is it free or extra ?
A: Yes, we could offer the sample for free charge but do not pay the cost of freight.
Q: What is your terms of payment ?
A: Payment 30%TT in advance. 70% T/T before shippment
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Rolling Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Bevel Wheel |
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 2/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
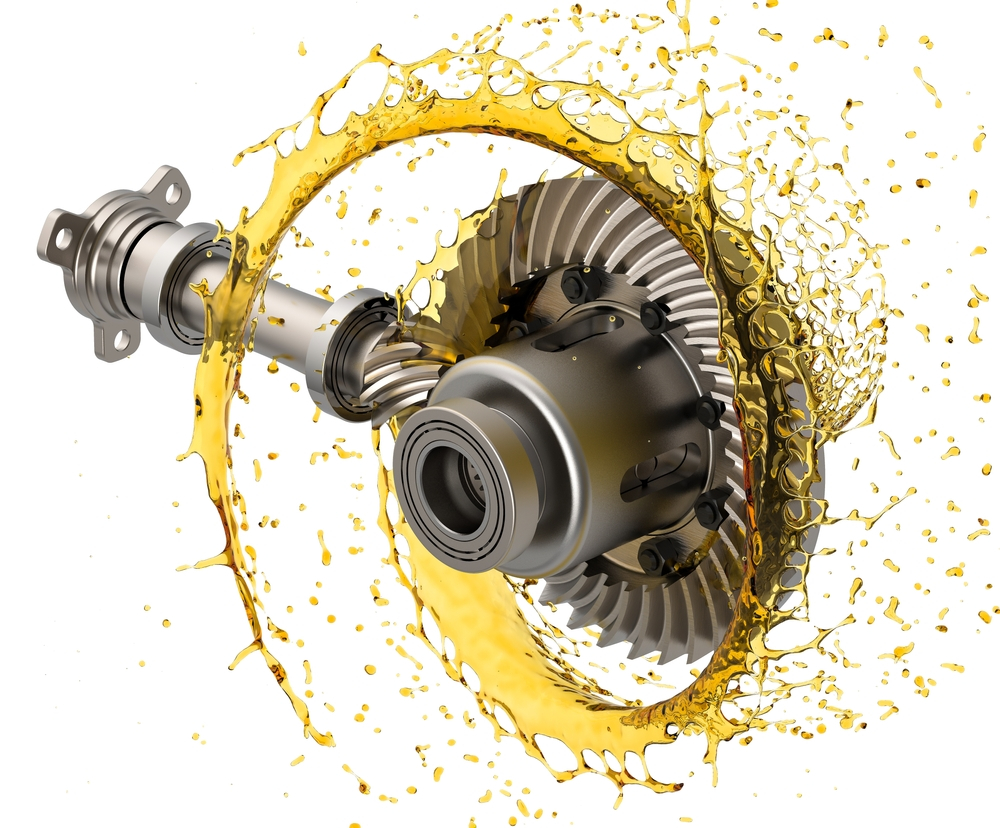

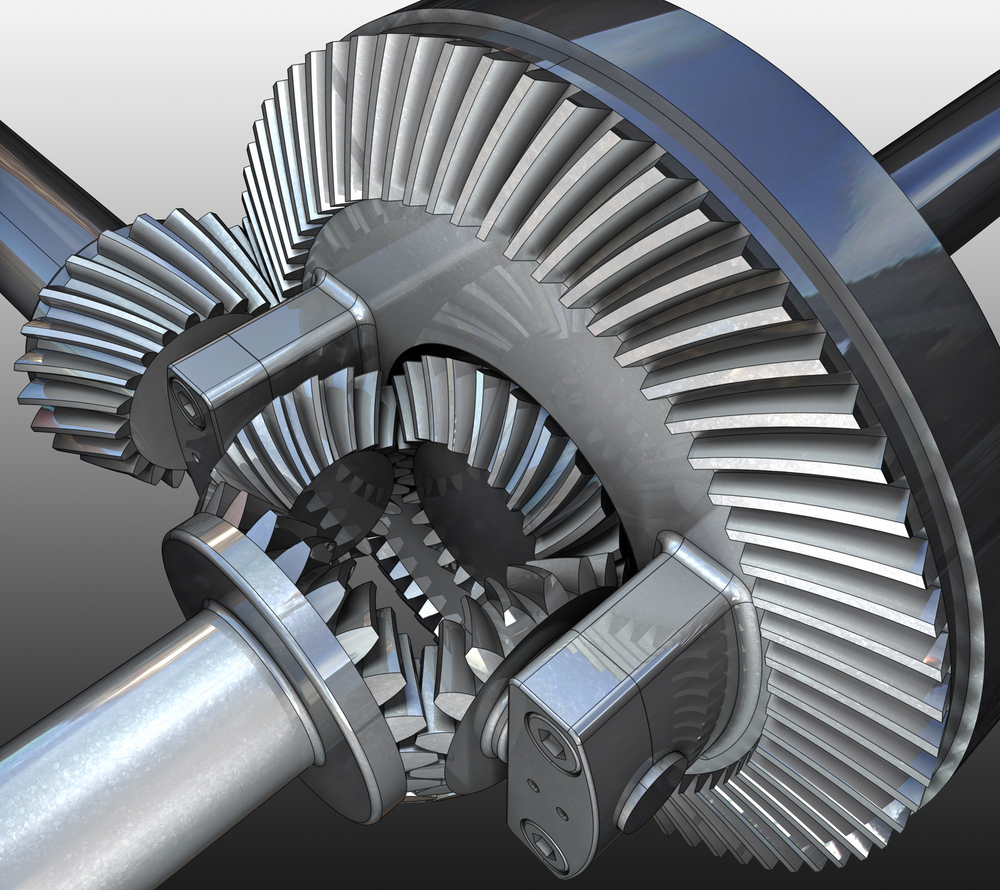
How does a differential gear distribute power between the wheels?
A differential gear is responsible for distributing power between the wheels of a vehicle, allowing them to rotate at different speeds while maintaining torque transfer. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a differential gear accomplishes this:
1. Power Input:
The differential gear receives power from the transmission or driveshaft connected to the engine. This power is transmitted to the differential assembly, which is typically located in the axle housing.
2. Ring and Pinion Gears:
Within the differential assembly, the power from the driveshaft is transferred to the ring and pinion gears. The ring gear is a large gear that surrounds the differential assembly, while the pinion gear is a smaller gear connected to the driveshaft. The interaction between these gears allows the power to be redirected.
3. Side Gears and Spider Gears:
The ring gear is connected to side gears, also known as bevel gears, through a set of small gears called spider gears. The side gears are attached to the axle shafts, which are responsible for transmitting power to the wheels. The spider gears allow the side gears to rotate independently of each other while maintaining torque transfer.
4. Differential Action:
As the vehicle moves, the differential gears enable the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns. When the vehicle is moving in a straight line, the spider gears rotate smoothly, allowing equal power distribution to both wheels. However, during a turn, the inside wheel travels a shorter distance than the outside wheel, causing them to rotate at different speeds.
5. Speed and Torque Distribution:
The differential gear adjusts the speed and torque distribution between the wheels based on their rotational differences. When the vehicle is turning, the spider gears allow one wheel to rotate faster than the other, ensuring that torque is transferred to the wheel with better traction. This allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds, preventing tire scrubbing and providing smooth cornering.
6. Limited-Slip and Locking Differentials:
In certain differential systems, such as limited-slip differentials or locking differentials, additional mechanisms are incorporated to enhance traction and power distribution. Limited-slip differentials use clutch packs or friction plates to provide a predetermined amount of resistance, allowing some speed differentiation between the wheels while still transferring power. Locking differentials, on the other hand, lock the side gears together, ensuring equal torque distribution to both wheels, regardless of traction conditions.
7. Differential Types:
There are various types of differentials, including open differentials, limited-slip differentials, electronic differentials, torque vectoring differentials, and more. Each type has its own mechanisms and technologies to distribute power between the wheels effectively, depending on the vehicle’s requirements and driving conditions.
In summary, a differential gear distributes power between the wheels by utilizing a system of gears, including ring and pinion gears, side gears, and spider gears. The differential action allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns, ensuring smooth cornering and preventing tire scrubbing. Additional mechanisms, such as limited-slip or locking differentials, can further enhance traction and power distribution in various driving conditions.
How do differential gears contribute to traction in slippery conditions?
In slippery conditions, such as driving on ice, snow, or wet surfaces, differential gears play a crucial role in improving traction and maintaining vehicle control. Here’s a detailed explanation of how differential gears contribute to traction in slippery conditions:
- Torque Distribution: Differential gears allow torque to be distributed between the wheels on the same axle. In slippery conditions, where traction is reduced, differential gears enable power to be sent to the wheels with better grip. This distribution of torque helps maximize traction and prevent wheel spin.
- Wheel Speed Variation: In slippery conditions, the wheels on the same axle may encounter different levels of traction. For example, one wheel might be on a patch of ice while the other is on a surface with better grip. Differential gears accommodate this variation by allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds. This wheel speed variation helps ensure that power is directed to the wheels with more traction, improving overall grip and stability.
- Slip Limitation: When one wheel loses traction and starts to slip, the other wheel with better grip can potentially receive less power due to the default behavior of an open differential. However, some differential systems employ advanced features like limited-slip differentials (LSD) or electronic traction control systems. These systems detect wheel slip and apply mechanisms to limit slip and redirect power to the wheel with better traction, effectively improving traction in slippery conditions.
- Positive Traction Devices: In some cases, differential gears can be equipped with positive traction devices such as locking differentials or electronic locking differentials. These devices lock the differential gears, forcing both wheels on the same axle to rotate at the same speed. This feature is particularly beneficial in extremely slippery conditions where maximum traction is essential. By locking the differential, these devices ensure that power is evenly distributed to both wheels, maximizing grip and traction.
- Off-Road Capability: Differential gears with advanced features like limited-slip differentials or locking differentials are commonly employed in off-road vehicles. These vehicles often encounter challenging terrain with low-traction conditions. The differential systems in these vehicles enhance off-road capability by transferring power to the wheels with the most traction, preventing wheel spin, and allowing the vehicle to navigate through difficult terrain more effectively.
In summary, differential gears contribute to traction in slippery conditions by distributing torque between wheels, accommodating wheel speed variation, limiting slip through advanced features, and offering positive traction devices. These mechanisms allow power to be directed to the wheels with better grip, improving traction, stability, and overall vehicle control in slippery conditions.
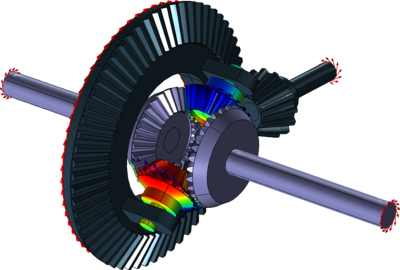
What are the functions of a differential gear in a vehicle?
A differential gear in a vehicle serves several important functions. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Torque Distribution:
One of the primary functions of a differential gear is to distribute torque (rotational force) from the engine to the wheels. As the engine generates power, the differential ensures that it is transmitted to the wheels efficiently and effectively. By dividing the torque between the two wheels, the differential enables both wheels to receive power and propel the vehicle forward.
2. Differential Action:
The differential gear allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds when the vehicle is turning or when one wheel encounters different traction conditions. This differential action is crucial for smooth and controlled maneuvering. By enabling the outer wheel to rotate faster than the inner wheel during a turn, the differential allows the vehicle to negotiate corners without binding or skidding.
3. Wheel Speed Compensation:
When the vehicle is turning, the inside wheel travels a shorter distance compared to the outside wheel. Without a differential, this speed difference would cause significant drivetrain stress and tire wear. The differential gear compensates for the varying wheel speeds by allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing strain on the drivetrain components.
4. Traction Improvement:
In situations where one wheel loses traction, such as when driving on slippery surfaces or uneven terrain, the differential gear helps improve traction. By allowing the wheel with traction to receive more power, the differential ensures that the vehicle can continue moving forward. This is particularly important in vehicles with two-wheel drive, as the differential helps optimize power delivery to the wheel with better traction.
5. Reducing Tire Wear:
The differential gear contributes to reducing tire wear by accommodating differences in wheel speeds. By allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns, the differential minimizes tire scrubbing and uneven wear. It helps distribute the forces evenly across the tires, promoting longer tire life and maintaining better overall traction.
6. Enhanced Stability and Handling:
The differential gear plays a crucial role in enhancing vehicle stability and handling. By allowing the wheels to rotate independently, the differential facilitates better control during turns and maneuvering. It helps maintain proper weight distribution, prevents excessive understeer or oversteer, and promotes balanced handling characteristics.
Overall, the differential gear is an integral component of a vehicle’s drivetrain, responsible for torque distribution, wheel speed compensation, traction improvement, reducing tire wear, and enhancing stability and handling. It enables smooth and efficient power delivery to the wheels while accommodating varying speed and traction conditions, resulting in improved performance and driving dynamics.


editor by CX 2024-04-02